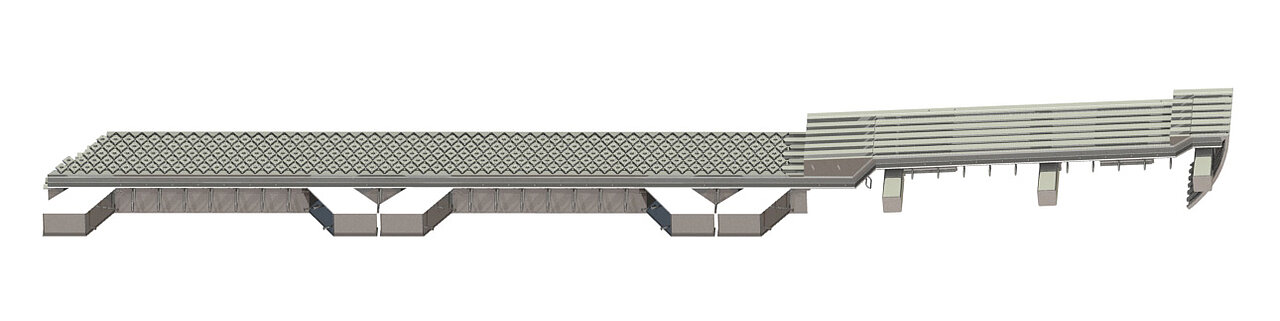
Expansion joints for roadway bridges
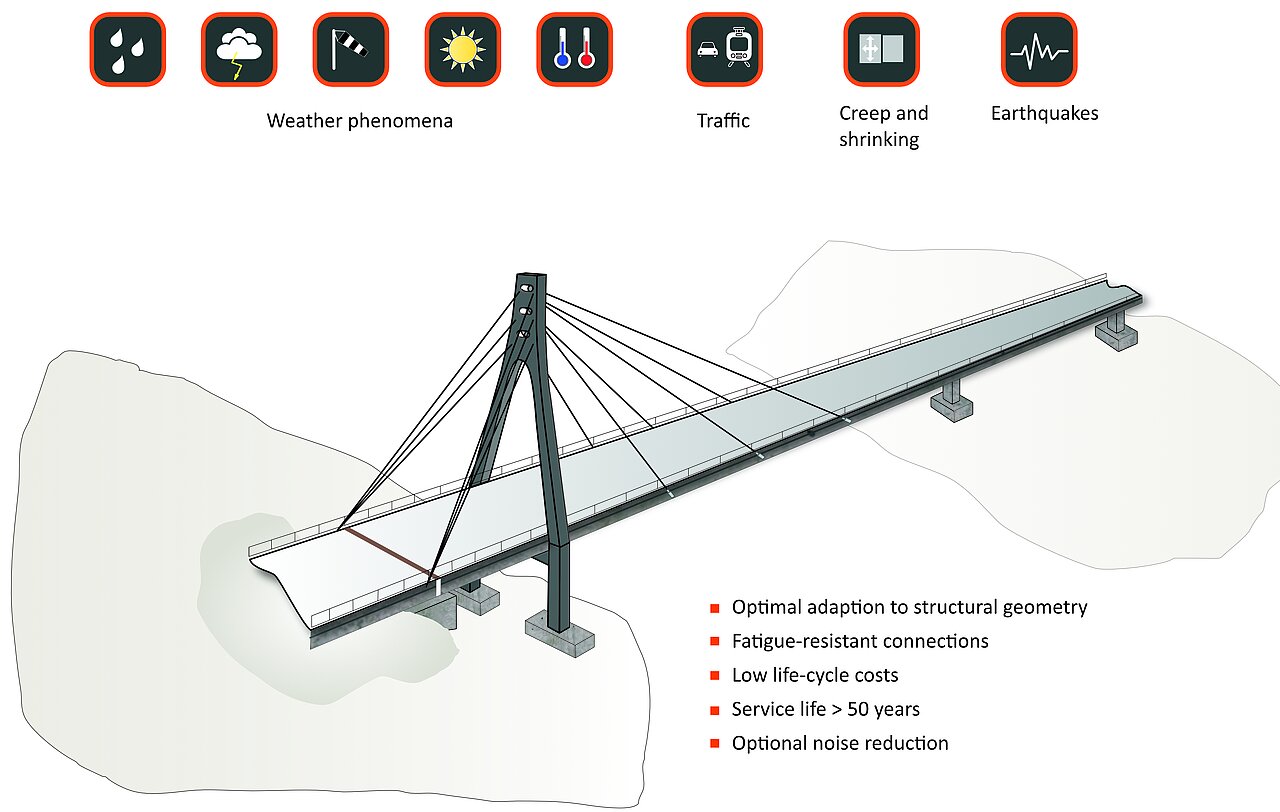
MAURER expansion joints are designed for heavy road traffic and allow, for example, creep and shrinkage displacements as well as movements due to temperature fluctuations, traffic and wind. For earthquake load cases, the expansion joint can be adapted to the project-specific displacements; also see Bridges under seismic stress.
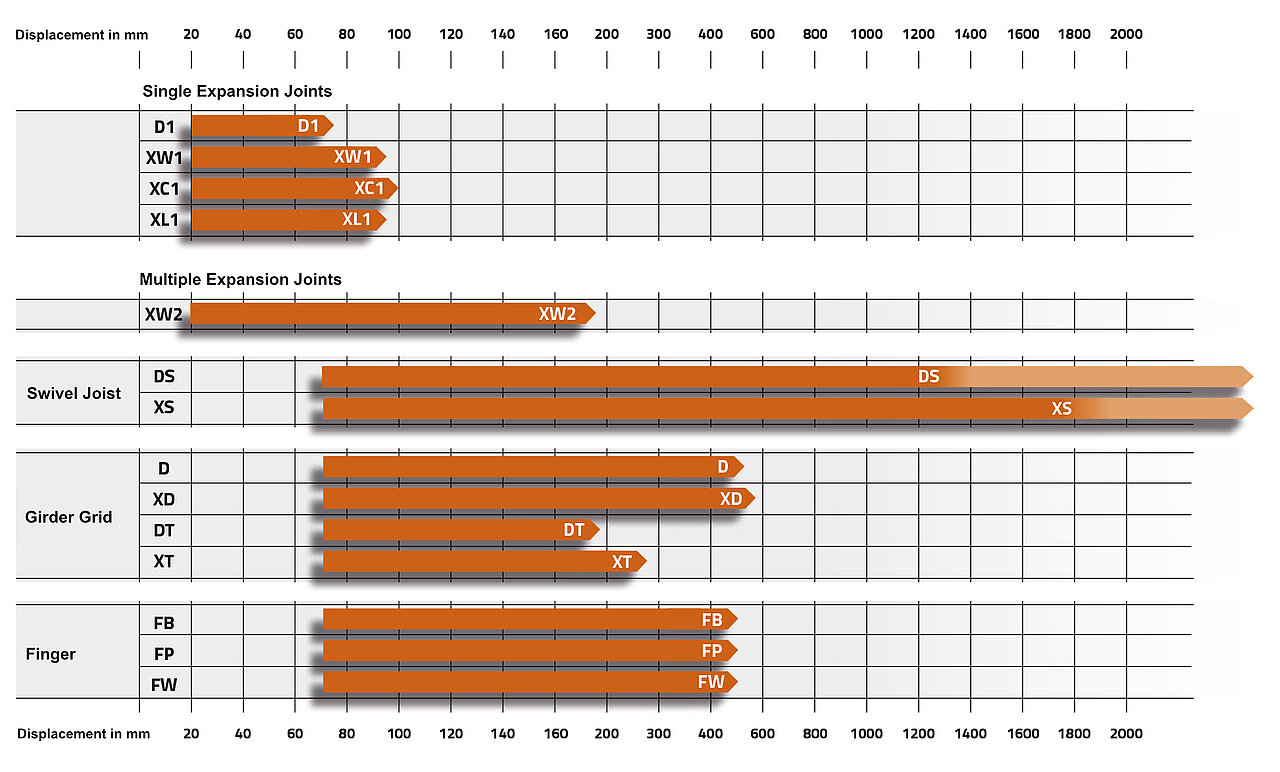
Strip joints – D1/XW1/XC1/XL1
MAURER strip joints for displacements of less than 100 mm are available in various versions. All versions fulfil separately the two main functions of fatigue resistant "firm solid anchoring" and "watertight connection". This enables the best possible adjustment of the two functions, the sealing profile and the edge structure, for the connection to the road and to the structure.
The modular joints for displacements greater than 100 mm are the most installed expansion joints in roadway bridges worldwide. A highly flexible modular system makes it possible to optimise the expansion joint geometry to the requirements of the structure.
Swivel joist expansion joints: DS, XS
Girder grid joints: DT, XT, D und XD
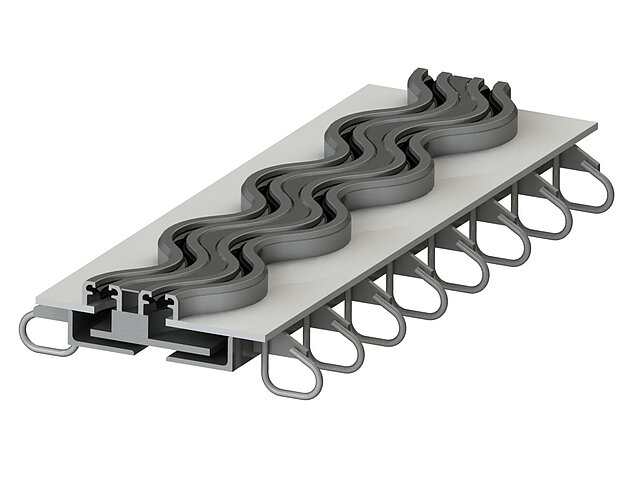
Two-wave-shaped expansion joint: XW2
- Load transfer into the structure without backlash-free effects via damping and pre-tensioned spring elements
- Fatigue-resistant connections
- Backlash-free displacements and force transmission minimises wear and increases reliability
- Ready-to-install complete unit, no complex on-site assembly required
- Can be individually configured for any degree of expansion longitudinally/transversely/vertically and in combination
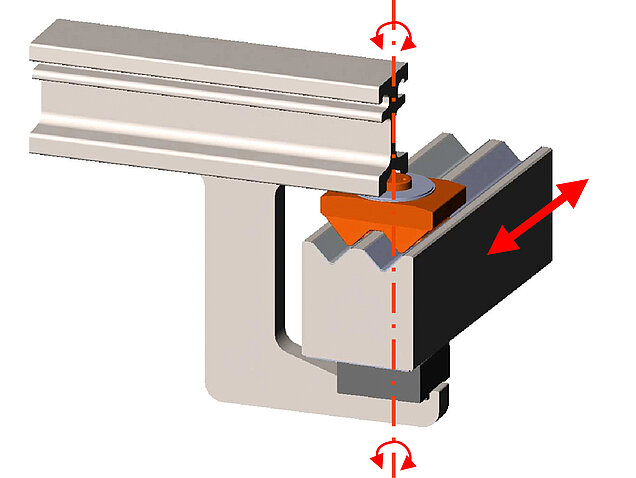
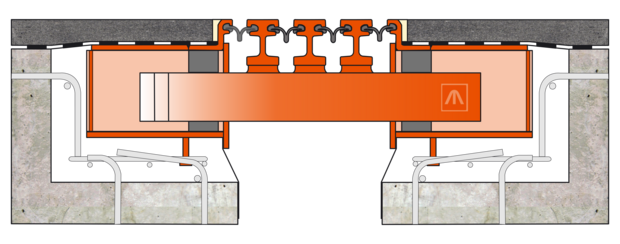
Catamaran guide with MSM®
Depending on the bridge displacements, the gap widths between the centre beams are distributed evenly. The special geometry and the pre-tensioned sliding spring prevent the sliding bearings from lifting off vertically.
- Precise kinematic control
- Unlimited fatigue resistance
- Flexible – six degrees of freedom without size restrictions
- Safe in traffic-permanent transmission of traffic loads
- Durable, backlash-free and low-friction sliding bearing
- Excellent cost-effectiveness and sustainability to material savings
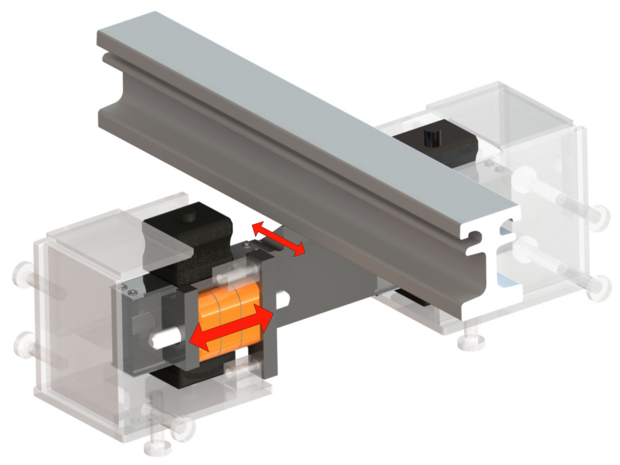
- The centre beams are controlled by control springs (polyurethane) that develop an increasing restoring force with increasing individual gap width (inverse control).
- Uniform distribution of the gap widths
- Limited displacements of max. ± 20 mm in the transverse direction and ± 10 mm in the vertical direction per centre beam
- Watertighness
- Fatigue-resistant
The XW2 joint was developed on the basis of the wave-shaped XW1 expansion joint. In addition to the wave-shaped edge profiles, the centre beam of the XW2 is also wave-shaped. This effectively eliminates the need for additional noise protection elements. The self-cleaning effect of the non-covered displacement gaps significantly reduces maintenance.