Expansion joints for railway bridges
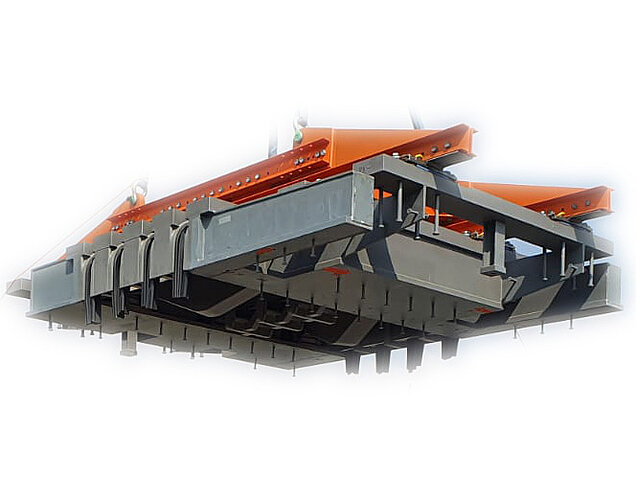
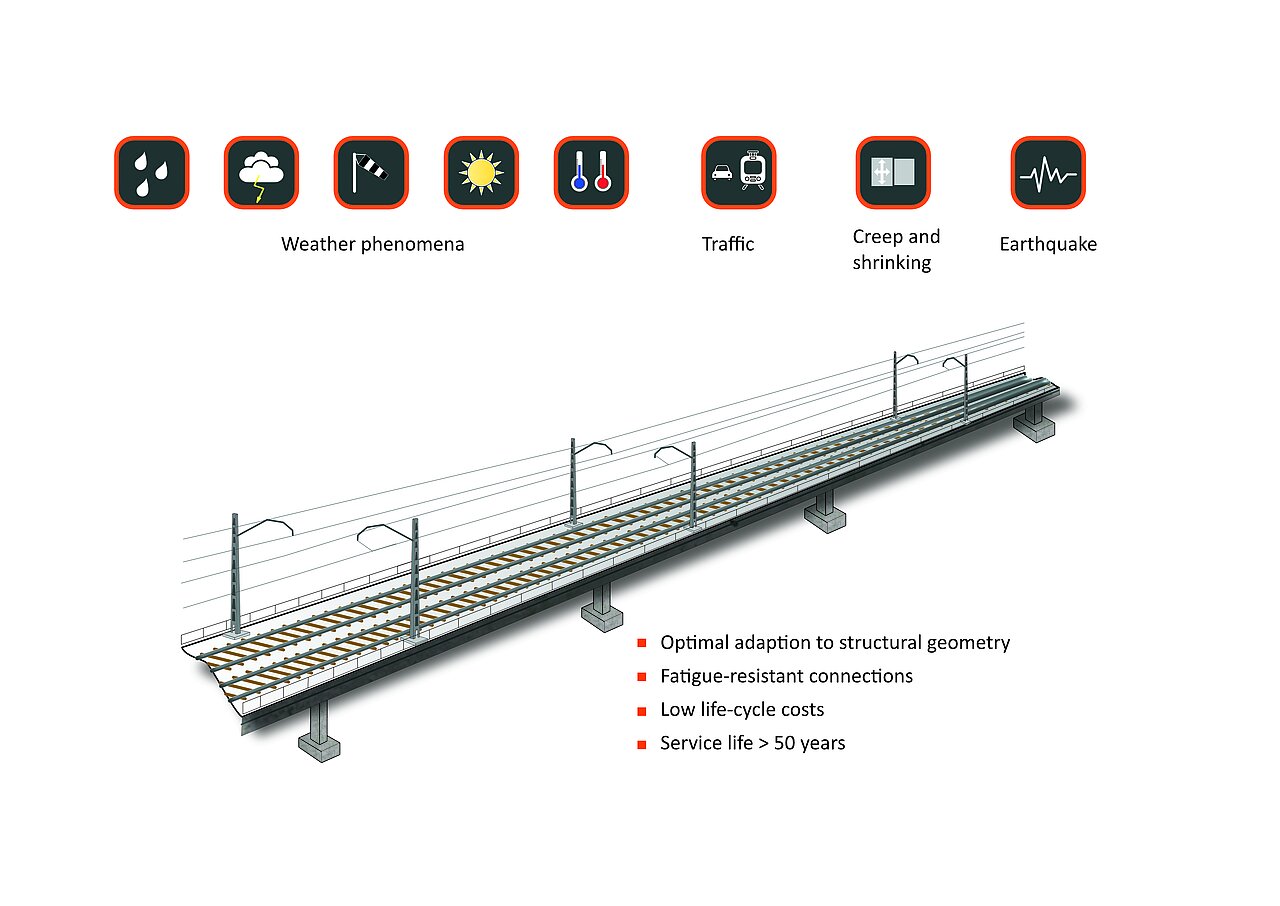
Railway bridges have different requirements for expansion joints than road bridges. Mat expansion joints are not driven over their surface directly and serve to seal the structure gap in a watertight manner while simultaneously absorbing the displacement and rotation of the superstructure. The traffic loads are usually transferred via the ballast bed.
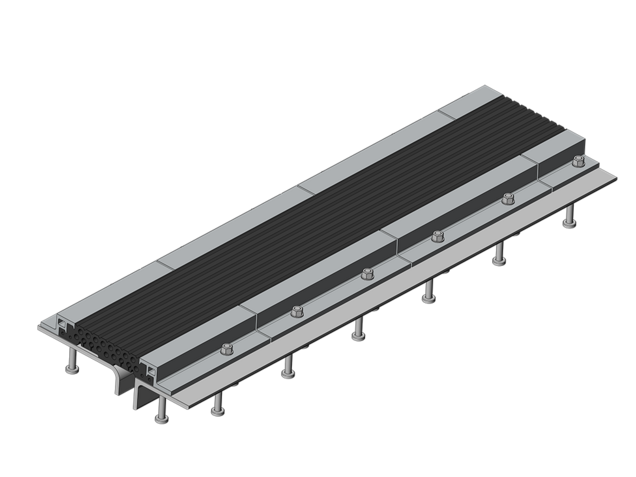
MAURER mat expansion joints are approved by DB AG (German Federal Railways) by means of a Manufacturer-Related Product Qualification (MRPQ). In contrast, the guided cross-tie for larger movements corresponds to a bridging construction over the structural gap, which, in addition to the superstructure displacements, directly absorbs and transfers the traffic loads.
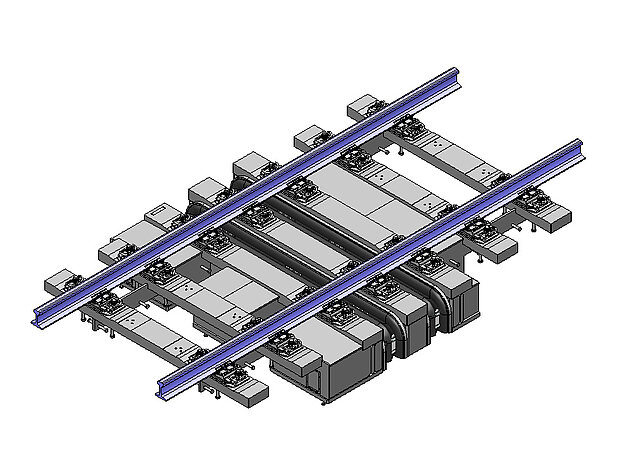
MAURER Type CT
- Adherence to the permissible rail support point forces and distances
- Safe transfer of any traffic loads up to 300kM/h
- Restraint-free accommodation of the displacements and rotations of the superstructure, regardless of direction and axis
- Service life > 60 years
- Delivery completely assembled
- Quick and easy installation
- Earthquake-resistant
- Watertightness